
|
BRHS /
Definitions And Risk Assessment PrinciplesThe objective of risk assessment is to evaluate the risk related to a specific activity for the purpose of managing this risk in an effective way. Definitions Safety management principlesTwo different safety management principles are possible: Consequence Based Safety Management will claim that the worst conceivable events at an installation processing hazardous materials should not have consequences outside certain boundaries, and will thus design safety systems to assure this. Risk Based Safety Management maintains that the residual risk should be analysed both with respect to the probabilities and the nature of hazard, and hence give information for further risk mitigation. This implies that very unlikely events might, but not necessarily will, be tolerated. Risk Based Safety ManagementRisk based safety management is the philosophy in line with central regulations and legislation in Western countries increasingly requiring risk assessment and documentation. The Risk Based Safety Management (often called risk management) principle is that some risks, specified through risk acceptance criteria, should be removed or reduced to meet safety requirements (residual risk level objectives). However, both prescriptive requirements (detailed standards) and goal-oriented requirements (risk based decisions) have a role to play in design of processes and installations. The Risk Based Safety Management is a systematic approach which measures risk through risk analysis methods and relates it to established risk acceptance criteria for the identification of design specifications or need for risk reduction measures. Beyond implementing risk reducing measures in order to meet tolerable risk level, such measures should also be implemented if further risk reduction can be obtained at costs lower than the benefits obtained. This is often referred to as the ALARP principle. They can either be consequence reducing measures or accident probability reducing measures. Probability reducing measures should be preferred. The principle is illustrated in the figure below 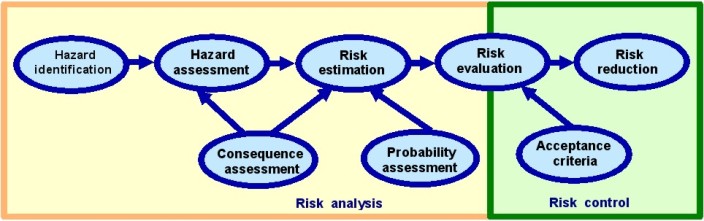 Figure: Risk Based Safety Management The ALARP principle - As Low As Reasonable PracticableBelow a certain risk level where where the hazard is in the unacceptable area and risk cannot be tolerated whatsoever; normally defined by risk acceptance criteria, the ALARP principle (As Low As Reasonable Practicable) should be applied in order to optimise risk reduction. In such cases cost benefit analyses should be used in order to evaluate different risk reducing options. Risk reducing measures should be implemented if the cost is not disproportoinate relative to the benefits of risk reduction. The ALARP principle is illustrated in the figure below 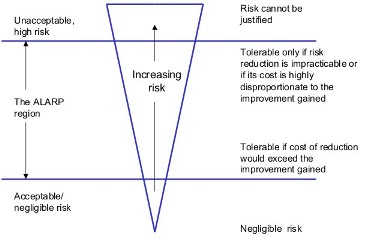 Figure: The ALARP principle Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA)QRA is a formalized mathematical method used in order to evaluate numerical individual, environmental, employee and public risk level values for comparison with regulatory risk criteria. Since satisfactory demonstration of acceptable risk levels is often a requirement for approval of major hazard plant construction plans, the use of QRA is important for such cases in order to indicate and take actions for risk minimization. However, even if QRA uses scientific methods and verifiable data, it does have uncertainties, limitations and application boundaries and therefore its use has to consider very carefully those aspects. That is why QRA is used as a complementary tool in decision making process, in areas where its strengths recommend it. << Accident Influence on the Environment] | [[BRHS/BRHS|Content | Risk Assessment Methodologies >> |